Need Help?
Be Aware of What can be expected after Brain Injury
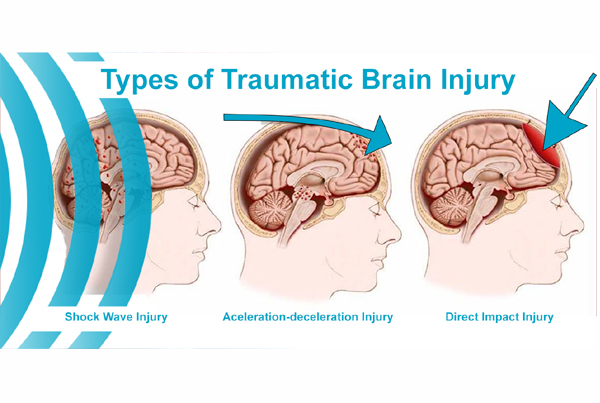
Be Aware of What can be expected after Brain Injury
The very thought of injury to the brain itself is traumatizing. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) refers to the destruction or damage of brain tissues because of a car crash, sudden fall, assault, gunshot wound, etc. Brain damage occurs due to a blow to the injured person's head, which whips the head backward and forwards or from one side to the other. In a car crash, specific areas like the temporal and frontal lobes of the brain seem to get damaged. Many individuals wish to know about post-brain injury effects as they hold a certain misconception about this particular matter.
Be aware of what can be expected to post a brain injury
Two kinds of effects are usually observed immediately after a TBI. The tissues of the injured individual's brain might react to trauma as well as lead to tissue damage along with a comprehensive series of physiological and biochemical responses. Certain things that were once safely housed in the cells might flood the brain after injury. Such a process results in further destroying and damaging brain cells and is termed secondary cell death.
The other type of effect is actually noticed in the injured person's functioning. People with extremely severe injuries may lose consciousness during the period of trauma. The state of unconsciousness might last from a fraction of minutes to many weeks or several months. Lengthy loss of consciousness is better known as the coma. Negative respiration changes and motor functions may also be produced just after few days of the trauma. Individuals with severe injuries may never regain consciousness, but others who will come to the conscious state may undergo certain neurologically-based signs like aggression, irritability, etc.
Just after a few weeks of a brain injury, the healthy functioning of brain tissues is slightly affected due to bleeding, swelling as well as a change in brain chemistry. The eyes of an injured person might stay closed post-injury, and he or she may not exhibit any positive signals of awareness. Slowly, with the decrease of swelling as well as blood flow along with an improvement of brain chemistry, the functioning of the brain tends to improve gradually.
Also, with proper treatment, the injured individual might seem to open his eyes slowly. Besides this, the sleep and wake cycle might also begin, and he or she may start to follow commands, provide a response to the members of the family, and speak.
In certain cases, a person may also enter into a minimally conscious state. This means he or she will stay partially conscious and also understand the source of visual and sound stimulation. Such a person can show signs of vocalization at times as well as an outburst of emotions. Later, during recovery stages, an individual can also develop various physical and brain functions and may regain the ability to respond gradually.
Get In Touch
Tags
- Dr. Arun Sharma Brain and Spine Clinic
- Pediatric Neurosurgery surgeon in Bhikaji Cama Place
- Pediatric Neurosurgery surgeon in Munirka
- Pediatric Neurosurgery surgeon in Vasant Vihar
- Brain and Spine Trauma Center in Munirka
- Brain and Spine Trauma Center in Vasant Kunj
- Brain and Spine Trauma Center in Vasant Vihar
- Brain and Spine Trauma Center in Lajpat nagar
- SPINE TUBERCULOSIS in saket
- SEIZURES in saket
- DEGENERATIVE SPINE treatment in saket
- Neck pain treatment in saket
- HEAD INJURY treatment in saket
- HOLISTIC HEALING in saket
- Pediatric Neurosurgery Surgeon in Greater Kailash
- Brain and Spine Trauma in Greater Kailash
- Spine Tuberculosis in Greater Kailash
- Seizure Treatment in Greater Kailash
- Degenerative Spine Treatment in Greater Kailash
- Neck Pain Treatment in Greater Kailash
- Heady Injury Treatment in Greater Kailash
- Holistic Healing in Greater Kailash
- Headache Pain Treatment in Greater Kailash
- Back Pain Treatment in Greater Kailash
- Spinal Tumors Treatment in Greater Kailash
- Lifestyle Management in Greater Kailash
- Behavioral Health in Greater Kailash
- Neurotherapy in Greater Kailash
- Pediatric Neurosurgery Surgeon in Bhikaji Cama Place
- Brain and Spine Trauma in Bhikaji Cama Place
- Spine Tuberculosis in Bhikaji Cama Place
- Seizure Treatment in Bhikaji Cama Place
- Degenerative Spine Treatment in Bhikaji Cama Place
- Neck Pain Treatment in Bhikaji Cama Place
- Heady Injury Treatment in Bhikaji Cama Place
- Holistic Healing in Bhikaji Cama Place
- Headache Pain Treatment in Bhikaji Cama Place
- Back Pain Treatment in Bhikaji Cama Place
- Spinal Tumors Treatment in Bhikaji Cama Place
- Lifestyle Management in Bhikaji Cama Place
- Behavioral Health in Bhikaji Cama Place
- Neurotherapy in Bhikaji Cama Place
- Pediatric Neurosurgery Surgeon in Munirka
- Brain and Spine Trauma in Munirka
- Spine Tuberculosis in Munirka
- Seizure Treatment in Munirka
- Degenerative Spine Treatment in Munirka
- Neck Pain Treatment in Munirka
- Heady Injury Treatment in Munirka
- Holistic Healing in Munirka
- Headache Pain Treatment in Munirka
- Back Pain Treatment in Munirka
- Spinal Tumors Treatment in Munirka
- Lifestyle Management in Munirka
- Behavioral Health in Munirka
- Neurotherapy in Munirka
- Pediatric Neurosurgery Surgeon in Vasant Vihar
- Brain and Spine Trauma in Vasant Vihar
- Spine Tuberculosis in Vasant Vihar
- Seizure Treatment in Vasant Vihar
- Degenerative Spine Treatment in Vasant Vihar
- Neck Pain Treatment in Vasant Vihar
- Heady Injury Treatment in Vasant Vihar
- Holistic Healing in Vasant Vihar
- Headache Pain Treatment in Vasant Vihar
- Back Pain Treatment in Vasant Vihar
- Spinal Tumors Treatment in Vasant Vihar
- Lifestyle Management in Vasant Vihar
- Behavioral Health in Vasant Vihar
- Neurotherapy in Vasant Vihar
- Pediatric Neurosurgery Surgeon in Vasant Kunj
- Brain and Spine Trauma in Vasant Kunj
- Spine Tuberculosis in Vasant Kunj
- Seizure Treatment in Vasant Kunj
- Degenerative Spine Treatment in Vasant Kunj
- Neck Pain Treatment in Vasant Kunj
- Heady Injury Treatment in Vasant Kunj
- Holistic Healing in Vasant Kunj
- Headache Pain Treatment in Vasant Kunj
- Back Pain Treatment in Vasant Kunj
- Spinal Tumors Treatment in Vasant Kunj
- Lifestyle Management in Vasant Kunj
- Behavioral Health in Vasant Kunj
- Neurotherapy in Vasant Kunj
- Pediatric Neurosurgery Surgeon in Lajpat Nagar
- Brain and Spine Trauma in Lajpat Nagar
- Spine Tuberculosis in Lajpat Nagar
- Seizure Treatment in Lajpat Nagar
- Degenerative Spine Treatment in Lajpat Nagar
- Neck Pain Treatment in Lajpat Nagar
- Heady Injury Treatment in Lajpat Nagar
- Holistic Healing in Lajpat Nagar
- Headache Pain Treatment in Lajpat Nagar
- Back Pain Treatment in Lajpat Nagar
- Spinal Tumors Treatment in Lajpat Nagar
- Lifestyle Management in Lajpat Nagar
- Behavioral Health in Lajpat Nagar
- Neurotherapy in Lajpat Nagar
- Pediatric Neurosurgery Surgeon in Saket
- Brain and Spine Trauma in Saket
- Spine Tuberculosis in Saket
- Seizure Treatment in Saket
- Degenerative Spine Treatment in Saket
- Neck Pain Treatment in Saket
- Heady Injury Treatment in Saket
- Holistic Healing in Saket
- Headache Pain Treatment in Saket
- Back Pain Treatment in Saket
- Spinal Tumors Treatment in Saket
- Lifestyle Management in Saket
- Behavioral Health in Saket
- Neurotherapy in Saket
- Pediatric Neurosurgery Surgeon in Malviya Nagar
- Brain and Spine Trauma in Malviya Nagar
- Spine Tuberculosis in Malviya Nagar
- Seizure Treatment in Malviya Nagar
- Degenerative Spine Treatment in Malviya Nagar
- Neck Pain Treatment in Malviya Nagar
- Heady Injury Treatment in Malviya Nagar
- Holistic Healing in Malviya Nagar
- Headache Pain Treatment in Malviya Nagar
- Back Pain Treatment in Malviya Nagar
- Spinal Tumors Treatment in Malviya Nagar
- Lifestyle Management in Malviya Nagar
- Behavioral Health in Malviya Nagar
- Neurotherapy in Malviya Nagar
- Pediatric Neurosurgery Surgeon in Kalkaji
- Brain and Spine Trauma in Kalkaji
- Spine Tuberculosis in Kalkaji
- Seizure Treatment in Kalkaji
- Degenerative Spine Treatment in Kalkaji
- Neck Pain Treatment in Kalkaji
- Heady Injury Treatment in Kalkaji
- Holistic Healing in Kalkaji
- Headache Pain Treatment in Kalkaji
- Back Pain Treatment in Kalkaji
- Spinal Tumors Treatment in Kalkaji
- Lifestyle Management in Kalkaji
- Behavioral Health in Kalkaji
- Neurotherapy in Kalkaji
- Pediatric Neurosurgery Surgeon in Defence Colony
- Brain and Spine Trauma in Defence Colony
- Spine Tuberculosis in Defence Colony
- Seizure Treatment in Defence Colony
- Degenerative Spine Treatment in Defence Colony
- Neck Pain Treatment in Defence Colony
- Heady Injury Treatment in Defence Colony
- Holistic Healing in Defence Colony
- Headache Pain Treatment in Defence Colony
- Back Pain Treatment in Defence Colony
- Spinal Tumors Treatment in Defence Colony
- Lifestyle Management in Defence Colony
- Behavioral Health in Defence Colony
- Neurotherapy in Defence Colony
- Pediatric Neurosurgery Surgeon in RK Puram
- Brain and Spine Trauma in RK Puram
- Spine Tuberculosis in RK Puram
- Seizure Treatment in RK Puram
- Degenerative Spine Treatment in RK Puram
- Neck Pain Treatment in RK Puram
- Heady Injury Treatment in RK Puram
- Holistic Healing in RK Puram
- Headache Pain Treatment in RK Puram
- Back Pain Treatment in RK Puram
- Spinal Tumors Treatment in RK Puram
- Lifestyle Management in RK Puram
- Behavioral Health in RK Puram
- Neurotherapy in RK Puram
- Pediatric Neurosurgery Surgeon in Nehru Place
- Brain and Spine Trauma in Nehru Place
- Spine Tuberculosis in Nehru Place
- Seizure Treatment in Nehru Place
- Degenerative Spine Treatment in Nehru Place
- Neck Pain Treatment in Nehru Place
- Heady Injury Treatment in Nehru Place
- Holistic Healing in Nehru Place
- Headache Pain Treatment in Nehru Place
- Back Pain Treatment in Nehru Place
- Spinal Tumors Treatment in Nehru Place
- Lifestyle Management in Nehru Place
- Behavioral Health in Nehru Place
- Neurotherapy in Nehru Place
- Pediatric Neurosurgery Surgeon in South Extension
- Brain and Spine Trauma in South Extension
- Spine Tuberculosis in South Extension
- Seizure Treatment in South Extension
- Degenerative Spine Treatment in South Extension
- Neck Pain Treatment in South Extension
- Heady Injury Treatment in South Extension
- Holistic Healing in South Extension
- Headache Pain Treatment in South Extension
- Back Pain Treatment in South Extension
- Spinal Tumors Treatment in South Extension
- Lifestyle Management in South Extension
- Behavioral Health in South Extension
- Neurotherapy in South Extension
- Pediatric Neurosurgery Surgeon in Green Park
- Brain and Spine Trauma in Green Park
- Spine Tuberculosis in Green Park
- Seizure Treatment in Green Park
- Degenerative Spine Treatment in Green Park
- Neck Pain Treatment in Green Park
- Heady Injury Treatment in Green Park
- Holistic Healing in Green Park
- Headache Pain Treatment in Green Park
- Back Pain Treatment in Green Park
- Spinal Tumors Treatment in Green Park
- Lifestyle Management in Green Park
- Behavioral Health in Green Park
- Neurotherapy in Green Park
- Pediatric Neurosurgery Surgeon in CR Park
- Brain and Spine Trauma in CR Park
- Spine Tuberculosis in CR Park
- Seizure Treatment in CR Park
- Degenerative Spine Treatment in CR Park
- Neck Pain Treatment in CR Park
- Heady Injury Treatment in CR Park
- Holistic Healing in CR Park
- Headache Pain Treatment in CR Park
- Back Pain Treatment in CR Park
- Spinal Tumors Treatment in CR Park
- Lifestyle Management in CR Park
- Behavioral Health in CR Park
- Neurotherapy in CR Park
- show more
- show less









